Why are landscapes beautiful?
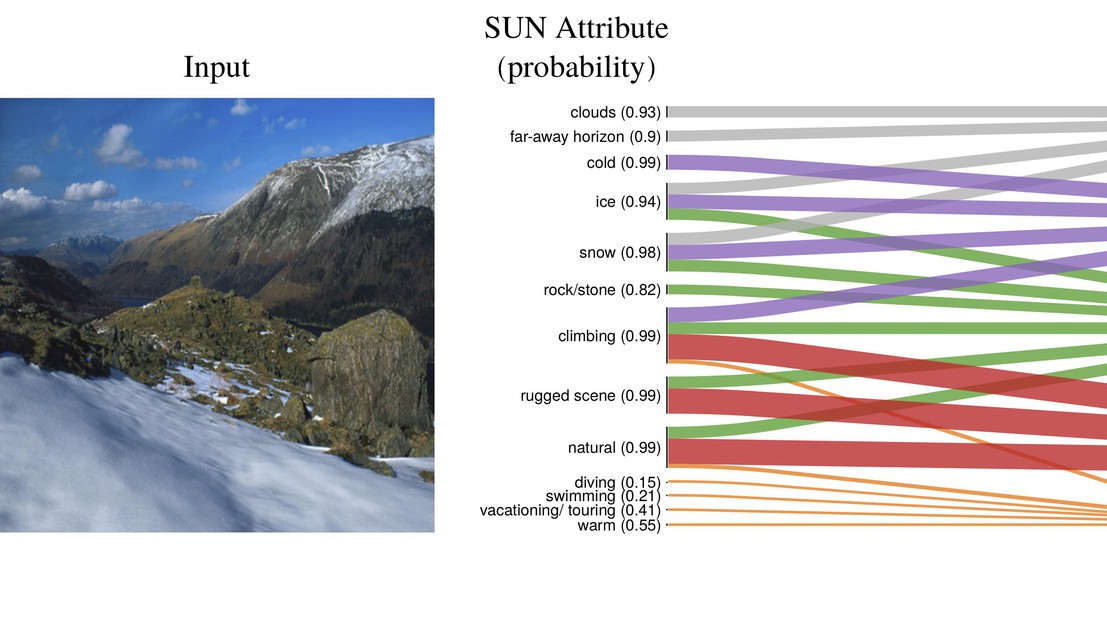
Example of theinterpretation of the beauty score on a mountain scene. © D. Marcos, 2020 / ACCV 2020 conference proceedings.
Researchers at ECEO used social media and machine learning to understand what people like in natural landscapes.
We definitely all have our own preferences: when it comes to holidays or just a day out, we chose our destination according to some perception of nature. In a way, we value nature and assign an ecosystem service to it. Landscape aesthetics is one such service and in two papers from ECEO, we studied how people look at lansdscapes and built models disentangling what made them like them.
We use deep learning, and tackle specificially the problem of interpretable AI. We learn from images of landscapes from the Web scored by volunteers which landscapes are considered beautiful. We do it automatically with neural networks.
Using a set of humanly understandable attributes (or concepts) we constrained the neural network to predict which attribute was found and used in the image and if its contribution to the beauty score was positive or negative. As such, the model results can now be interpreted. In other words, the black box is open.
Joint works with Wageningen University (Netherlands), Université de Bretagne du Sud (France), Ecole Polytechnique (France), Université de Paris (France) and Oxford University (U.K.).
- D. Marcos, S. Lobry, R. Fong, N. Courty, R. Flamary, and D. Tuia. Contextual semantic interpretability. In Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), 2020.
- P. Arendsen, D. Marcos, and D. Tuia. Concept discovery for the interpretation of landscape scenicness. Mach. Learn. Knowledge Extraction (MAKE), 2(4): 397-413.