Congratulations to Marco for his JACS paper!
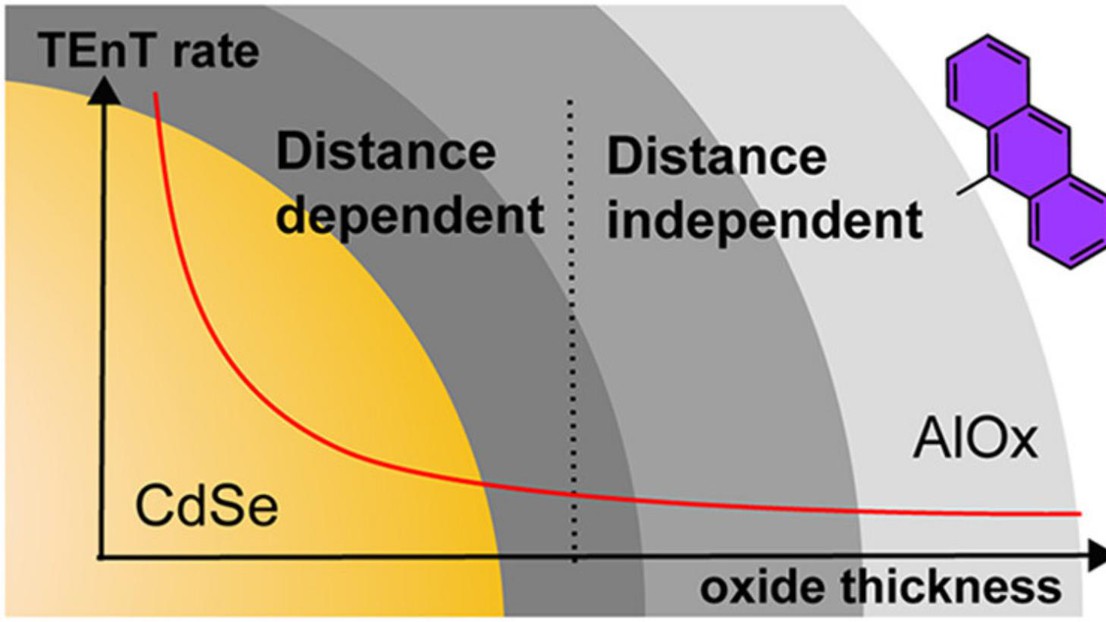
© c-ALD-Grown Metal Oxide Shell Enables Distance-Independent Triplet Energy Transfer from Quantum Dots to Molecular Dyes - CC-BY 4.0
Curious to learn more about designing efficient photocatalysts based on quantum dots?
Understanding how quantum dots interact with molecular dyes is central to advancing applications in light harvesting and photocatalysis. Herein, we synthesize CdSe@AlOx core@shell QDs and investigate their interaction with polyaromatic hydrocarbon. We uncover a nearly distance-independent triplet energy transfer extending up to ~2 nm, enabled by defects in the oxide shell that act as mediating states. The use of colloidal atomic layer deposition allows precise tuning of shell thickness and highlights the role of oxides in preserving QD properties while optimizing long-range QD–dye interactions. These insights establish oxide shells as powerful design elements to control charge and energy transfer in hybrid nanocomposites.
Read more here!
This publication was created as part of NCCR Catalysis, a National Centre of Competence in Research funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation.
c-ALD-Grown Metal Oxide Shell Enables Distance-Independent Triplet Energy Transfer from Quantum Dots to Molecular Dyes, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 34, 31409–31416