Mohammad's work now is in Journal of Physical Chemistry C!
© 2021 EPFL
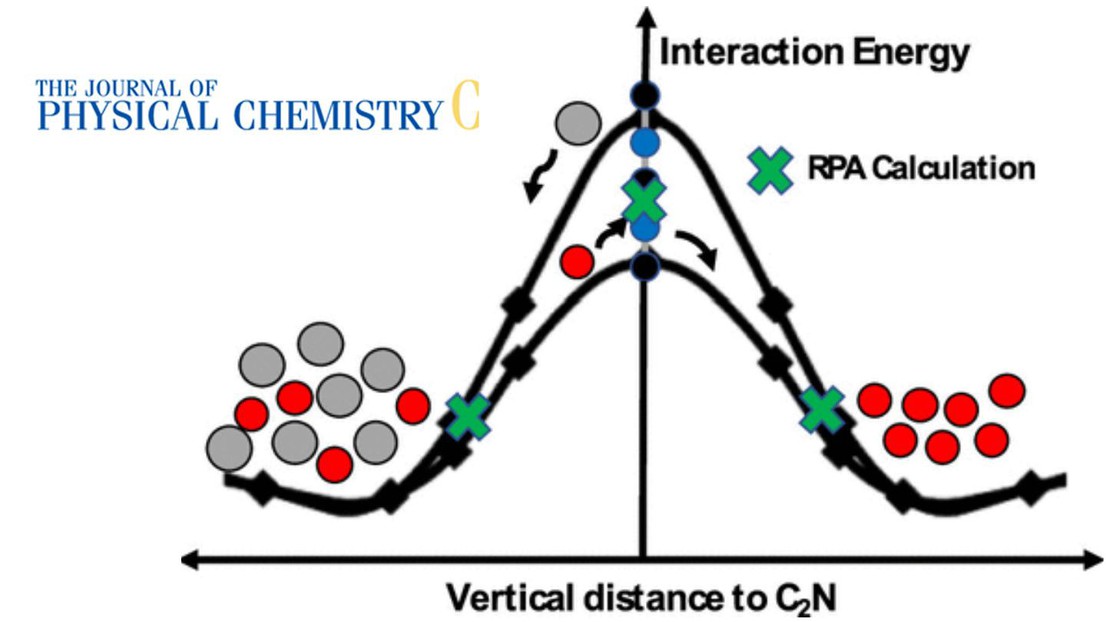
His novel work on the simulation of investigating the accurate calculation of potential energy surfaces for He, H2, N2, and CO2 across C2N nanopores, to characterize the gas-sieving potential of C2N has been published in Journal of Physical Chemistry C!
C2N is an ordered two-dimensional carbon nitride with 3.1 Å-sized nanopores, making it promising for high-flux gas sieving for energy-efficient He and H2 purification. We compare the potential energy surface derived from density-functional theory calculations using five commonly used van der Waals (vdW) approximations. While all five functionals point that the C2N nanopore yields He/N2 and H2/N2 selectivities over 1000, adsorption energies and energy barriers vary remarkably depending on the approximation chosen. We compare the calculations against the results from the adiabatic connection fluctuation dissipation theory, with random-phase approximation, known to be accurate in capturing vdW interactions. The comparison indicates that the interaction energy is less accurate with vdW density functional theory.