Freddy Radtke's research in "Immunity"
A study in the field of lymphocyte development and transformation from Freddy Radtke's lab published in "Immunity"...
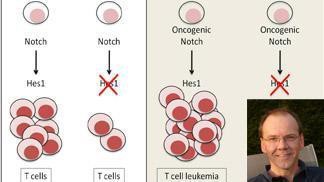
The development of the immune cell in the hematopoietic system is a highly controlled process, and aberrant regulation can lead to leukemia. The Notch signalling pathway is an important mechanism for cell-to-cell communication during embryonic development of a number of tissues, and also of their maintenance in the adult. It works through interactions of a membrane-associated ligand of the Delta or Jagged protein families on one cell with a receptor of the Notch family on the neighboring cell. While these extracellular interactions for the activation of Notch are well described, the intracellular signals that they induce are still poorly understood. Using conditional knock-out studies, a publication from the Radtke lab in the journal Immunity now shows that Notch stimulates T cell development through activation of the gene regulator Hes1. This effect is highly specific, as other known Notch-induced responses like thymocyte maturation are not affected. The data also suggests that Hes1 is essential for the development and maintenance of Notch-induced T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Reference: "Hes 1 Is a Critical but Context-Dependent Mediator of Canonical Notch Signaling in Lymphocyte Development and Transformation". Wendorff, A.A., Koch, U., et al (2010) Immunity, 33, 1-14