New discovery: nanometric imprinting on fiber
© 2017 EPFL
Researchers at EPFL have come up with a way of imprinting nanometric patterns on the inside and outside of polymer fibers. These fibers could prove useful in guiding nerve regeneration and producing optical effects, for example, as well as in eventually creating artificial tissue and smart bandages.
Researchers at EPFL’s Laboratory of Photonic Materials and Fibre Devices, which is run by Fabien Sorin, have come up with a simple and innovative technique for drawing or imprinting complex, nanometric patterns on hollow polymer fibers. Their work has been published in Advanced Functional Materials.
The potential applications of this breakthrough are numerous. The imprinted designs could be used to impart certain optical effects on a fiber or make it water-resistant. They could also guide stem-cell growth in textured fiber channels or be used to break down the fiber at a specific location and point in time in order to release drugs as part of a smart bandage.
Stretching the fiber like molten plastic
To make their nanometric imprints, the researchers began with a technique called thermal drawing, which is the technique used to fabricate optical fibers. Thermal drawing involves engraving or imprinting millimeter-sized patterns on a preform, which is a macroscopic version of the target fiber. The imprinted preform is heated to change its viscosity, stretched like molten plastic into a long, thin fiber and then allowed to harden again. Stretching causes the pattern to shrink while maintaining its proportions and position. Yet this method has a major shortcoming: the pattern does not remain intact below the micrometer scale. “When the fiber is stretched, the surface tension of the structured polymer causes the pattern to deform and even disappear below a certain size, around several microns,” said Sorin.
To avoid this problem, the EPFL researchers came up with the idea of sandwiching the imprinted preform in a sacrificial polymer. This polymer protects the pattern during stretching by reducing the surface tension. It is discarded once the stretching is complete. Thanks to this trick, the researchers are able to apply tiny and highly complex patterns to various types of fibers. “We have achieved 300-nanometer patterns, but we could easily make them as small as several tens of nanometers,” said Sorin. This is the first time that such minute and highly complex patterns have been imprinted on flexible fiber on a very large scale. “This technique enables to achieve textures with feature sizes two order of magnitude smaller than previously reported,” said Sorin. “It could be applied to kilometers of fibers at a highly reasonable cost.”
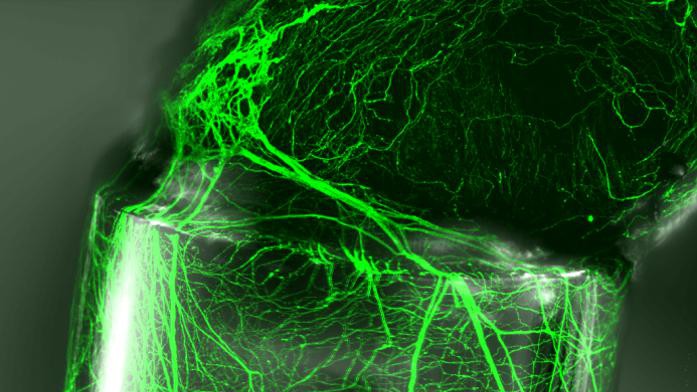
To highlight potential applications of their achievement, the researchers teamed up with the Bertarelli Foundation Chair in Neuroprosthetic Technology, led by Stéphanie Lacour. Working in vitro, they were able to use their fibers to guide neurites from a spinal ganglion (on the spinal nerve). This was an encouraging step toward using these fibers to help nerves regenerate or to create artificial tissue.
This development could have implications in many other fields besides biology. “Fibers that are rendered water-resistant by the pattern could be used to make clothes. Or we could give the fibers special optical effects for design or detection purposes. There is also much to be done with the many new microfluidic systems out there,” said Sorin. The next step for the researchers will be to join forces with other EPFL labs on initiatives such as studying in vivo nerve regeneration. All this, thanks to the wonder of imprinted polymer fibers.


