"Dupont des Matériaux" Award 2013 - Peter Cuony

© 2013 EPFL
Optical Layers fo Thin-film Silicon Solar Cells. Thesis EPFL n° 5190 (2011). Dirs.: Christophe Ballif & Matthieu Despeisse
"For the synthesis of a new class of functional filamentous silicon oxide nanomaterials, for having elucidated their properties and showing their beneficial properties when incorporated into optoelectronic thin film devices such as silicon based solar cells."
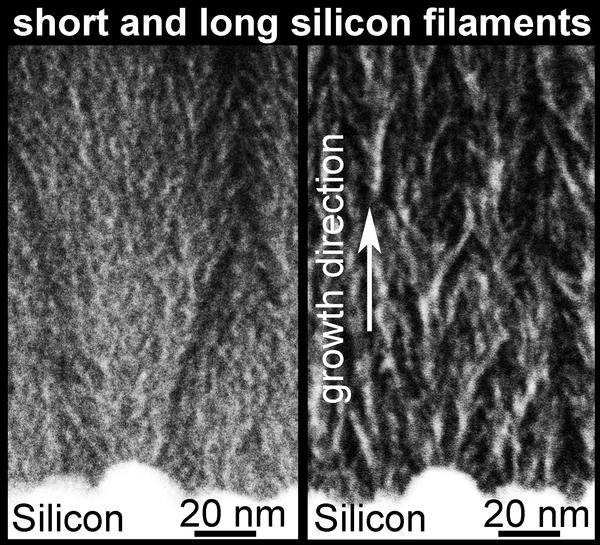
Abstract: Considering that silicon is the second most abundant element in the earth’s crust, and that 86 PW of solar radiation reach the earth’s surface—5,700 times more than the worldwide power consumption—silicon-based photovoltaics are clearly an excellent candidate to satisfy sustainably our future energy needs. However, photovoltaic conversion efficiencies still have to be increased and production costs reduced. Towards these goals, we present an inexpensively fabricated new class of silicon/silicon oxide (Si/SiOy~2) mixed-phase nanomaterials with independently tunable optical and electrical properties. With energy-filtered transmission electron microscopy, we show them to consist of nanometer-wide silicon filaments embedded in silicon oxide. In thin-film silicon solar cells, such filamentous SiOx helps reducing absorption losses in the doped layers, and its tunable refractive index allows for advanced light management by engineering reflection or anti-reflection effects within the cell. When undoped, the silicon filaments show similar quantum confinement effects as spherical silicon particles in silicon oxide, but their elongated forms and the low temperature deposition processes at 200 °C could facilitate device fabrication in all-silicon quantum “dot” photovoltaics and other optoelectronic applications (e.g. by allowing direct fabrication on conductive substrates).
Full Text: Optical Layers for Thin-film Silicon Solar Cells